Using the latest technology and incorporating the best practices gathered from Oracle's customers, Oracle Fusion Applications is a suite of 100% open standards-based business applications that provide a new standard for the way businesses innovate, work, and adopt technology. Delivered as a complete suite of modular, service-enabled enterprise applications, Oracle Fusion Applications works with Oracle's Applications Unlimited portfolio to evolve business to a new level of performance. Whether it is one module, a product family, or the entire suite, Oracle provides businesses with their choice of all advancements pioneered by Oracle Fusion Applications, at a pace that matches individual business demands.
- Standard Based Architecture
- Best Practices Business Processes
- Choice of Deployment options
Oracle Fusion Applications have been designed to ensure your enterprise can
be modeled to meet legal and management objectives. The decisions about your
implementation of Oracle Fusion Applications are affected by your:
• Industry
• Business unit requirements for autonomy
• Business and accounting policies
• Business functions performed by business units and optionally,
centralized in shared service centers
• Locations of facilities
Oracle EBS vs Oracle Fusion Apps:
BPEL (also known as BPEL4WS or WS-BPEL), the Business Process Execution Language is an
XML based programming tool for language service composition.
Fusion Applications uses BPEL wherever process logic is implemented. BPEL replaces Oracle
Workflow. So where in EBS Releases 11i & 12 a process is organized by Oracle Workflow, in Fusion Applications BPEL is used. For example the GL journal approval is handled by Oracle Workflow in Release 12. In Fusion Applications this is done via a BPEL process.
Oracle Fusion Apps:
Oracle Fusion Financials Applications:
1.
Oracle Fusion
Financials, which include general ledger, receivables, payables, asset
tracking, expense management, and cash management functionality.
2.
Oracle Fusion
Accounting Hub, providing the integration and reporting platform to effectively
drive a coexistence strategy with your existing financial systems.
Oracle Fusion
Financials provide features for:
1.
Receivable and
collection functionality within the Order Fulfillment process
2.
Asset accounting and
reporting within the Asset Life cycle Management process
3.
Cash management
functionality within both the Order Fulfillment and Procurement processes
4.
Payable and payment
functionality within the Procurement process
5.
Financial Control and
Reporting including taxation, subledger accounting, general ledger,
consolidation, and reporting functionally
6.
Expenses management
functionality within the Compensation Management process
7.
Multi-GAAP compliance
including approaches for simultaneous compliance with corporate and national
regulators and standards.
8.
Currency compliance
including capabilities for accounting in denomination and accounting currencies
and for translation to functional or reporting currencies as required in
compliance with the relevant principles within both the International Financial
Reporting Standards (IFRS) and United States Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles (GAAP).
.
Oracle Fusion Financials Phases:
Oracle Fusion Financials Phases:
To set
up your companies, ledgers, and business units (BUs), Oracle Fusion
Applications provide the Functional Setup Manager. The Functional Setup Manager
empowers enterprises to decentralize the change management process and enables
business users to change Oracle Fusion applications to fit their evolving
business needs.
Functional Setup Manager:
Functional Setup Manager:
- Provides a predefined, guided list of tasks for a full end-to-end visibility to all setup requirements enabling business users with self-service to implement quickly what they need and when they need it.
- Provides configurability of the Oracle Fusion offerings to mold the offerings to fit the business needs.
- Provides export and import capability to let companies setup one instance and reuse it several times.
- Provides a guided process making it easy to navigate through planning, implementation, deployment, and ongoing maintenance.
- Provides a set of comprehensive reports to give full visibility to setup at any time.
- Getting Started
- Setting Up the Task List
Manager
- Setting Up Import and Export
- Maintaining the Functional
Manager
1.
Plan and Configure phase: (Getting Started)
- Plans and discovers what
offerings, options, and features are available in Oracle Fusion
applications
- Researches the requirements
- Analyzes the impact of the
change
- Selects the most suitable
offering, options, and features based on the requirements
- Creates the implementation
project and assigns tasks
2. Implementation phase
a) Setting up the Task List Manager
- Reviews and executes assigned
setup tasks
- Updates the status of the tasks
- Adds attachments and notes
- Validates the implementation.
b) Setting up Import and Export
·
Creates configuration
packages and exports setup data
·
Imports the
configuration package in another instance
·
Analyzes setup data
report
3. Maintaining the
Functional Manager
- Maintains the environment with
ongoing setup changes
- Updates setups due to event or time-based changes
Financial
Sub-ledger Architectures: Sub ledger architecture includes
- Dashboard and work areas
- Invoice imaging
- Tax
- Sub-ledger accounting
- Reconciling subledger accounts
All Oracle Fusion
Financials applications deploy dashboards. On a dashboard, work areas display
tabulations of the tasks that a given role needs to accomplish. These are
updated by incoming work load in real time. In Payables, for example, newly
scanned invoices are tabulated for the Payables Specialist to process. In
General Ledger, the accounts monitored by the accountant are updated at each
journal posting. In Receivables, new invoices and receipts pending further
actions are listed for the Billing Specialist and Receivables Specialist to
process. The tabulations are designed
to be easily adjusted to suit your needs in several ways and can be modified,
prioritized, and even replaced.
The work areas monitor
processes and provide updates on status. Items awaiting approval, for example,
are listed, as are items with issues, such as incomplete invoices and unposted
journals. Social tools are available, so that any person who needs to act, such
as an approver, can be contacted immediately. The tabulations support searching
by example, saved searches, export to spreadsheet, and other actions, so that
the work can be moved along without using menus or navigating away from the
work area.
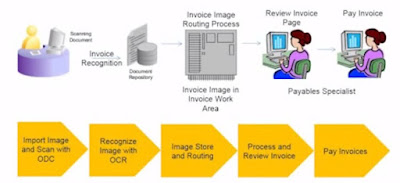
Invoice imaging:
In Oracle Fusion, image
scanning is not just a plug in or add-on. The accounts payable process has been
re-architectured to simplify data capture and eliminate work costs and
activities.
You can scan the
invoice from any location, The scanned
invoice is routed to the shared service center in any part of the world for
centralized processing. The image is read by the system through smart optical
character recognition centrally and the invoice data pages are largely
prepopulated from the images. Imaging and routing facilitates speedy
processing, as the invoice is complete and appears immediately in the work area
of the Accounts Payables (AP) specialists. The AP specialists can compare the
image and the data before approving it. Oracle Fusion Applications manages the
file network system, document repository, image processing server, and the
routing process with little or no human involvement.
Oracle Fusion Tax Architecture:
There
are many kinds of transaction taxes, including sales tax, value-added tax
(VAT), goods and services tax (GST), and customs duties.
The tax architecture includes the following tiers:
- Tax Configuration: Foundation
- Tax Determining Factors
- Tax Configuration: Advanced
- Services
- Tax Management
- Tax regimes and taxes, such as GST, VAT, and sales tax
- Tax jurisdiction and tax authorities, such as California and Ireland
- Tax status of different types of transactions, such as taxable or nontaxable transactions
- Tax rates including recovery rates
The Tax Determining
Factors tier identifies the factors that participate in determining the tax
on an individual transaction. These taxability factors are:
- Parties to the transaction,
such as your companies, vendors, and customers
- Products such as food, books,
automobiles, and furniture, with each product having a different tax
arrangement
- Places of shipment and delivery
- Business processes involved,
such as sales, purchases, and inventory management
For example, you could be a legal entity registered for tax
in Illinois and selling a product to another legal entity that is registered in
Toronto. To sell your product, you must take into account, the following taxes:
- Illinois sales taxes
- US export taxes
- Canadian import taxes
- Toronto taxes
The Tax Configuration:
Advanced
tier leads you away from mainstream compliance into specialist cases. For
example, the advanced configuration includes setting up tax rules to determine:
- Tax regimes
- State sales tax versus a
national customs tax
- Shipment and delivery details
- Registrations, both yours and
your customers and vendors
- Tax basis that results from the
combinations of the above considerations
- Tax rates and recovery rates
Tax
or recovery is calculated based on these and other factors. Tax recovery uses
the Services tier to return the appropriate tax or recovery for the product to
the entity requesting it. Other services include setup and partner integration
services. Third-party tax partners deliver external data, such as tax rates,
simplifying your tax processing.
The Tax Management tier includes:
- Transaction taxes and related
data that are stored in tax repositories and are delivered with reports.
Standard reports are provided that you can use or copy to customize to
meet your tax reporting requirements.
- Configuration data that is
stored in a configuration repository. Tax records are stored in a tax
record repository.
Sub-ledger
Accounting Architecture:
Oracle Fusion Sub ledger Accounting takes data from both external and oracle fusion applications and accounts for that data in oracle fusion general ledger, populating the balances cube and preparing data for the sophisticated reporting capabilities available in the General ledger.
Sub ledger accounting uses a set of rules that it applies to sub ledger transaction data to determine the accounts to which the data is posted and to format & present the entries appropriately, using the rules the subledger accounting engine generates sub ledger journals and stores them in the sub ledger accounting repository as the preceding figure illustrates. It creates sub-ledger balances by customer and vendors. Sub-ledger accounting populates the sub-ledger balances and creates general ledger journals based on the frequency details and formatting options that you specify. The general ledger journals are recorded in the general ledger balance table and cube.
Sub-ledger Accounting is capable of generating entries for the same data according to different rules, facilitating reporting compliance to different conventions, such as statutory and corporate, or such as the old and the new principles when a new accounting principle is promulgated. It is anticipated that the Convergence of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) will involve retrospective reporting under Leases, Revenue Recognition, and Financial Instruments for all US GAAP and IFRS filing groups.
Financial Control and Reporting:
The Financial Control and Reporting process delivers greater control of your enterprise financial management activities. It provides key users with better visibility of the entire process -- from capturing transactions and closing sub-ledgers to financial consolidation and reporting processes. The process provides greater accuracy in updating and reconciling general ledger accounts, with checks and balances across all subledger systems.
Reference: https://docs.oracle.com/en/ and https://support.oracle.com, Fusion user guide and implementation guides.












