Oracle E-Business Suite and Oracle Cloud Applications are two different Enterprise Resource Solutions (ERP) provided by Oracle to ease your day to day business processes and there will always be a confusion whether to choose Oracle E-Business Suite Applications or Oracle Cloud Applications. Before finding out difference between Oracle E-business Suite and Oracle Cloud first have a brief overview about both these Oracle ERP.
Oracle’s E-Business Suite (EBS) is the on-premise traditional solution for Oracle ERP. It consists of a collection of modules, all integrated into one suite. When we use the term ‘Oracle EBS,’ assume it to be on-premise unless otherwise noted.
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Applications is a suite of next generation enterprise solutions developed by Oracle Corporation. It provides services in financial management, human capital management, customer relationship management, supply chain management, procurement, project portfolio management etc. Cloud/Fusion Applications is a best of the breed combination of features and functionalities taken from Oracle E-Business Suite, JD Edwards, PeopleSoft and Siebel product lines. The suite is built on the top of the Oracle Fusion Middleware technology stack. It is based on Service Oriented Architecture (SOA).
Oracle Cloud Approach:
Oracle’s recommended cloud approach depends on the customer and their existing state
ERP CLOUD (SAAS) Approach - If you don’t have a current on-premise Oracle EBS implementation and you are more of an small or medium size business(SMB), then Oracle recommends that you go directly to ERP cloud.
Co-existing Approach - If you are an enterprise with an on-premise Oracle EBS implementation, Oracle recommends that you go with the coexistence approach. Keep your existing Oracle EBS on-premise.
The cloud ERP is not mature enough yet and cannot support complex and heavily customized business processes. Second, Oracle is acknowledging the heavy investments customers have
made on their existing EBS.
However, there are two main scenarios on which Oracle does recommend existing customers to start implementing cloud applications: scenarios on which Oracle does recommend existing customers to start implementing cloud applications
If you have a new subsidiary , Oracle recommends that instead of implementing another EBS instance, you implement the system on the Oracle ERP Cloud and then integrate them into your headquarters EBS, which is on-premise.
If you want to implement new modules or re-implement modules, such as HCM, Sales or Marketing, Projects Suite Oracle recommends that you do so on their cloud and integrate them to your core on-premise EBS (e.g. Finance & Logistics).
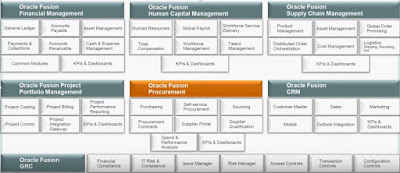
Breadth and Depth:
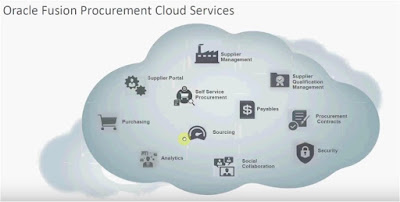
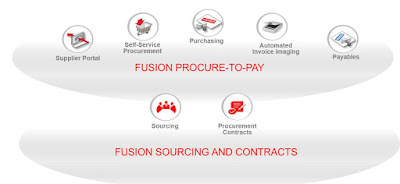
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Procurement Management:
Oracle Cloud Inventory Management:
Supply Chain Management: Supply Chain Management is known as SCM, it is the failure to notice of resources, data, and finance as they flow in a process from supplier to the manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to buyer. It involves coordinating and integrating cycle flows among companies. It is said that the final goal of any effective supply chain management system is to lower the breakdowns.
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Procurement: Fusion Procurement is a system code which allows an organization to automate the processes of purchasing goods and maintaining an inventory of goods or services. Procurement can generate requisition, approval, purchase orders, goods receipt note, execute the ordering process online, invoice creation to products received, and pay all bills in online.
Human Capital Management: Human Capital Management is known as HCM, it is an approach to employee staffing that perceives people as human capital assets whose current value can be evaluated and next generation value can be improved through investment.
Customer Relationship Management: Customer Relationship Management is a term which refers to practices, technologies, and strategies that an organization used to manage and analyze user interactions and data throughout the consumer lifecycle, with the aim of increasing business relationships with end-users, assisting in user maintenance and driving sales growth. It is intended to gather information on customers across many different channels of contact between the seller and the buyer who includes the company’s fax, website, phone, live chat, email, social media, and marketing materials. It provides buyer facing staff detailed information on customer’s personal information, purchase history, buying preferences.
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Financials: Oracle Fusion Financials revolutionizes and information access with real-time intelligence and native. It is a complete financial management system which includes a wide range of modules including general ledger, account payables and receivables, fixed assets, and cash management. It is a standard-based platform to help end users to improve their business processes.
Governance, Risk, and Compliance: GRC is software process which allows openly held companies to design and manage technical operations that focus on regulating. GRC naturally combines applications that control the basic functions of GRC into an integrated wrap. It enables an organization to follow a systematic way and organized method for managing GRC related pla
Coexistence provides an opportunity for organizations to
choose the best from existing and available systems and incrementally adopt new
solutions without the expense of a complete overhaul. These integration flows have transformation, routing, API calls, and
logging information built into the software to provide complete business
process integration. (Cloud to Cloud, Cloud to on-Premise).
The diagram below illustrate the OER process to discover and upload files with the data you wish to import into Oracle ERP Cloud Service.
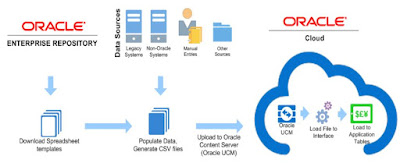
Integrating large amounts of data to cloud-based applications can be challenging. Access to the Cloud/Fusion Applications database is not available, making it difficult to access reference data needed to perform transformations and inserts into staging and open interface tables.
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Applications has delivered the File Based Data Import (FBDI) feature to facilitate the integration of data into Cloud/Fusion Applications.
The process of using FBDI is
1.Download a Microsoft Excel template that identifies all of the fields.
2.Populate the spreadsheet with data from the external system.
3.Save the file as a .csv file type. (Zip file)
4.Upload the file to the server.
5.Run processes to transfer the data to the interface tables and import into the various applications.
All of the data is validated during import to ensure its integrity. The manual FBDI approach works great for smaller sets of data that can be easily entered and manipulated in a spreadsheet. However, for larger volumes of data, where complex transformations have to take place between a source application and the Oracle cloud/Fusion Application, or where the data integration happens on a regular basis, a more robust and automated approach may be necessary.
Integration using Web Services:
Oracle’s E-Business Suite (EBS) is the on-premise traditional solution for Oracle ERP. It consists of a collection of modules, all integrated into one suite. When we use the term ‘Oracle EBS,’ assume it to be on-premise unless otherwise noted.
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Applications is a suite of next generation enterprise solutions developed by Oracle Corporation. It provides services in financial management, human capital management, customer relationship management, supply chain management, procurement, project portfolio management etc. Cloud/Fusion Applications is a best of the breed combination of features and functionalities taken from Oracle E-Business Suite, JD Edwards, PeopleSoft and Siebel product lines. The suite is built on the top of the Oracle Fusion Middleware technology stack. It is based on Service Oriented Architecture (SOA).
Oracle Cloud Approach:
Oracle’s recommended cloud approach depends on the customer and their existing state
ERP CLOUD (SAAS) Approach - If you don’t have a current on-premise Oracle EBS implementation and you are more of an small or medium size business(SMB), then Oracle recommends that you go directly to ERP cloud.
Co-existing Approach - If you are an enterprise with an on-premise Oracle EBS implementation, Oracle recommends that you go with the coexistence approach. Keep your existing Oracle EBS on-premise.
The cloud ERP is not mature enough yet and cannot support complex and heavily customized business processes. Second, Oracle is acknowledging the heavy investments customers have
made on their existing EBS.
However, there are two main scenarios on which Oracle does recommend existing customers to start implementing cloud applications: scenarios on which Oracle does recommend existing customers to start implementing cloud applications
If you have a new subsidiary , Oracle recommends that instead of implementing another EBS instance, you implement the system on the Oracle ERP Cloud and then integrate them into your headquarters EBS, which is on-premise.
If you want to implement new modules or re-implement modules, such as HCM, Sales or Marketing, Projects Suite Oracle recommends that you do so on their cloud and integrate them to your core on-premise EBS (e.g. Finance & Logistics).

Ø
Dashboards and work areas put information in one
place
Ø
Spreadsheet integrations
Ø
Transaction processing
Ø
Mobile
Ø
Management and reporting
Ø
Setup for fast, simple implementation
Oracle Cloud Financial Management
Breadth and Depth:
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Procurement Management:


Oracle Cloud Inventory Management:
Oracle Fusion/Cloud is known as Oracle Cloud Application
which is next generation suite of software application which is distributed
across various groups, which includes a broad range of Cloud/fusion application
modules like Enterprise Resource Planning, Oracle Cloud Procurement, Supply
Chain Management, Customer Relationship Management, Human Capital Management,
Cloud Financials, Governance, Risk and Compliance.
Enterprise Resource Planning:
Enterprise Resource Planning is also referred as ERP, which is an industry term
for the wide range of actions that helps a firm to handle their financial
business. The main goal of enterprise resource planning is to assist the flow
of information so that business decisions can be data-driven. The software
suites are designed to collect and administrate data from various levels of
industries to offer management with insight into key act indicators in
real-time.Supply Chain Management: Supply Chain Management is known as SCM, it is the failure to notice of resources, data, and finance as they flow in a process from supplier to the manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to buyer. It involves coordinating and integrating cycle flows among companies. It is said that the final goal of any effective supply chain management system is to lower the breakdowns.
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Procurement: Fusion Procurement is a system code which allows an organization to automate the processes of purchasing goods and maintaining an inventory of goods or services. Procurement can generate requisition, approval, purchase orders, goods receipt note, execute the ordering process online, invoice creation to products received, and pay all bills in online.
Human Capital Management: Human Capital Management is known as HCM, it is an approach to employee staffing that perceives people as human capital assets whose current value can be evaluated and next generation value can be improved through investment.
Customer Relationship Management: Customer Relationship Management is a term which refers to practices, technologies, and strategies that an organization used to manage and analyze user interactions and data throughout the consumer lifecycle, with the aim of increasing business relationships with end-users, assisting in user maintenance and driving sales growth. It is intended to gather information on customers across many different channels of contact between the seller and the buyer who includes the company’s fax, website, phone, live chat, email, social media, and marketing materials. It provides buyer facing staff detailed information on customer’s personal information, purchase history, buying preferences.
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Financials: Oracle Fusion Financials revolutionizes and information access with real-time intelligence and native. It is a complete financial management system which includes a wide range of modules including general ledger, account payables and receivables, fixed assets, and cash management. It is a standard-based platform to help end users to improve their business processes.
Governance, Risk, and Compliance: GRC is software process which allows openly held companies to design and manage technical operations that focus on regulating. GRC naturally combines applications that control the basic functions of GRC into an integrated wrap. It enables an organization to follow a systematic way and organized method for managing GRC related pla
Pre Packaged Integration:
The diagram below illustrate the OER process to discover and upload files with the data you wish to import into Oracle ERP Cloud Service.

Integrating large amounts of data to cloud-based applications can be challenging. Access to the Cloud/Fusion Applications database is not available, making it difficult to access reference data needed to perform transformations and inserts into staging and open interface tables.
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Applications has delivered the File Based Data Import (FBDI) feature to facilitate the integration of data into Cloud/Fusion Applications.
The process of using FBDI is
1.Download a Microsoft Excel template that identifies all of the fields.
2.Populate the spreadsheet with data from the external system.
3.Save the file as a .csv file type. (Zip file)
4.Upload the file to the server.
5.Run processes to transfer the data to the interface tables and import into the various applications.
All of the data is validated during import to ensure its integrity. The manual FBDI approach works great for smaller sets of data that can be easily entered and manipulated in a spreadsheet. However, for larger volumes of data, where complex transformations have to take place between a source application and the Oracle cloud/Fusion Application, or where the data integration happens on a regular basis, a more robust and automated approach may be necessary.
Integration using Web Services:
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Applications exposes many web services which
can be used to build inbound integration.
Cloud/Fusion Applications is expected to expose web services
that are available for external use. The list of available Web Services and
Business Events are published in Oracle Enterprise Repository (OER). Though
Oracle Cloud/Fusion Applications are designed using the Service-Oriented
Architecture (SOA) principles.
Composers:
There are 5
dimensions to making Enterprise Application changes, split by a combination of
intent and technology behind them. Cloud/Fusion Applications, via its underlying
middleware, includes a Composer tool for making adjustments in each dimension.
Having separate composers allows each to be relatively simple to use, increases
governance over changes, and speeds deployment. The 5 dimensions are:
The functionality provided by the composers the following is a short list of the most common customization-type requirements and which composer supports it:

Oracle Cloud UX RDK :
The Oracle Cloud UX RDK is for those who design and build SaaS simplified UIs and extensions using Oracle Application Development Framework (Oracle ADF) and deploy apps using Oracle Java Cloud Service and/or Oracle Java Cloud Service-SaaS Extensions (JCS-SX).
Oracle JET UX RDK :
The Oracle JET UX RDK is for those who design and build simplified UIs using Oracle JavaScript Extension Toolkit (JET). This RDK supports any JavaScript-suitable IDE or editor and supports deploying PaaS apps to a cloud server.
Oracle MAF UX RDK :
The Oracle MAF UX RDK is for those who design and build mobile apps using Oracle Mobile Application Framework (Oracle MAF). This RDK supports popular devices and native device features. Apps built using this RDK can also be integrated with Oracle Mobile Cloud Service.
Source: Oracle Cloud implementation and user guide, oracle support central notes.
Page Composer, Data
Composer, process composer, BI Composer & Application Composer (at present
for CRM).
The functionality provided by the composers the following is a short list of the most common customization-type requirements and which composer supports it:
· Change a Page Layout for one or more
users (Page Composer)
· Discover, Implement, and Add Seed
Data to Flexfields (Page Composer)
· Add a new Field onto a page (Page
Composer)
· Change Field Labels (Data Composer)
· Create new fields for an existing or
new business object (Data Composer)
· Change a BPEL process and adjust the
Human Workflows (Process Composer)
· Add and adjust reports to include
new attributes and data sources (BI Composer)
All
supported customizations and extensions are stored and applied in the context
of
Meta Data Services (MDS) Layer.
MDS defines the context for which the customization
will be applied over the
standard features at runtime. Some commonly used examples of
MDS layers are
a User, a Job Role, an Organization, or across a
whole Site

Oracle Cloud UX RDK :
The Oracle Cloud UX RDK is for those who design and build SaaS simplified UIs and extensions using Oracle Application Development Framework (Oracle ADF) and deploy apps using Oracle Java Cloud Service and/or Oracle Java Cloud Service-SaaS Extensions (JCS-SX).
Oracle JET UX RDK :
The Oracle JET UX RDK is for those who design and build simplified UIs using Oracle JavaScript Extension Toolkit (JET). This RDK supports any JavaScript-suitable IDE or editor and supports deploying PaaS apps to a cloud server.
Oracle MAF UX RDK :
The Oracle MAF UX RDK is for those who design and build mobile apps using Oracle Mobile Application Framework (Oracle MAF). This RDK supports popular devices and native device features. Apps built using this RDK can also be integrated with Oracle Mobile Cloud Service.
Source: Oracle Cloud implementation and user guide, oracle support central notes.








